BLOG
From URL to IRL: Four Pillars of Experiential Design for the Future of Offline Retail
As consumers begin returning to in-person shopping, it’s time for retailers to revisit the role of physical retail stores.
The last few years saw a boom in e-commerce, with innovations such as shoppable live streams, virtual try-ons and AI-powered recommendations enhancing the online retail experience. Today, as consumers re-enter physical stores, retailers can seize the opportunity to reimagine what in-person shopping looks like in the future of retail.
Consumers’ shopping behaviors have changed. Physical stores are no longer simply places of transaction. Instead, they can serve as storytelling centers that bring brands to life. Offline retail can help customers learn about products, provide an experience value and create stronger relationships. Customers like to view stores as places to experience something unique, memorable and human.
Also, brands must be clear on their story and audience when designing spaces and their content to create an in-store experience. Once the retail strategy is clear, it’s all about execution. To create a distinct offline experience, brands must think critically about what experiences are only possible in person and how technology can be leveraged to deliver them.
Below are four areas for brands to consider when developing an experiential design for the future of offline retail:
1. Beyond POS: Cultivating Community at the Storefront
It’s time to think beyond transactions. Having a physical footprint in today’s world can be so much more for a brand than simply a point-of-sale. Stores can become multi-purpose spaces dedicated to activities and brand activations that create a sense of community. Customers can come to a store to discover and learn about a brand and touch and feel its products.
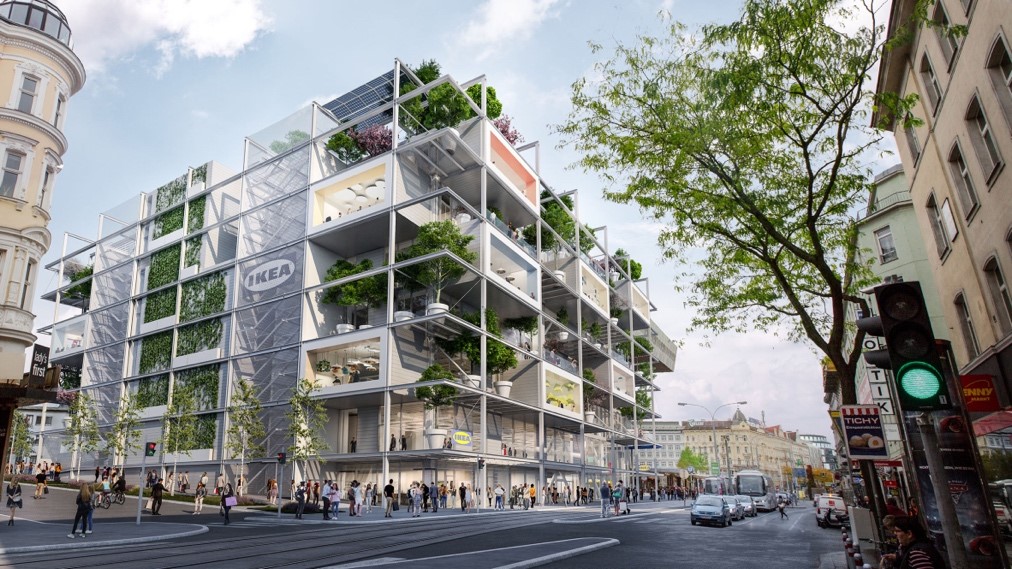

IKEA has long been known for its one-of-a-kind in-store experience, with its winding paths, tiny model homes and world-famous meatballs. Its new store in Vienna takes it one step further. Rather than the giant blue warehouse that customers are used to, this 7-story structure of stacked glass pods and covered in greenery was designed to resemble the brand’s minimalist shelving units. Inside, the building offers a public rooftop terrace in addition to a hostel and café. Shoppers can shop, scan and pay directly from the IKEA mobile app and have larger items delivered to their homes via emission-free electric vehicles. IKEA plans for this new store to be more than a shopping center; instead, it’s meant to serve as an urban hub for people to gather in the heart of the city center.
2. In-Store Analytics: Connecting the Data Dots
Retail stores are also untapped data mines for brands. By leveraging technology that can track customer behavior in stores, brands can improve the offline journey for their consumers and even create personalized shopping experiences. This behind-the-scenes investment can give brands valuable data about how their customers shop as well as help better predict future trends.
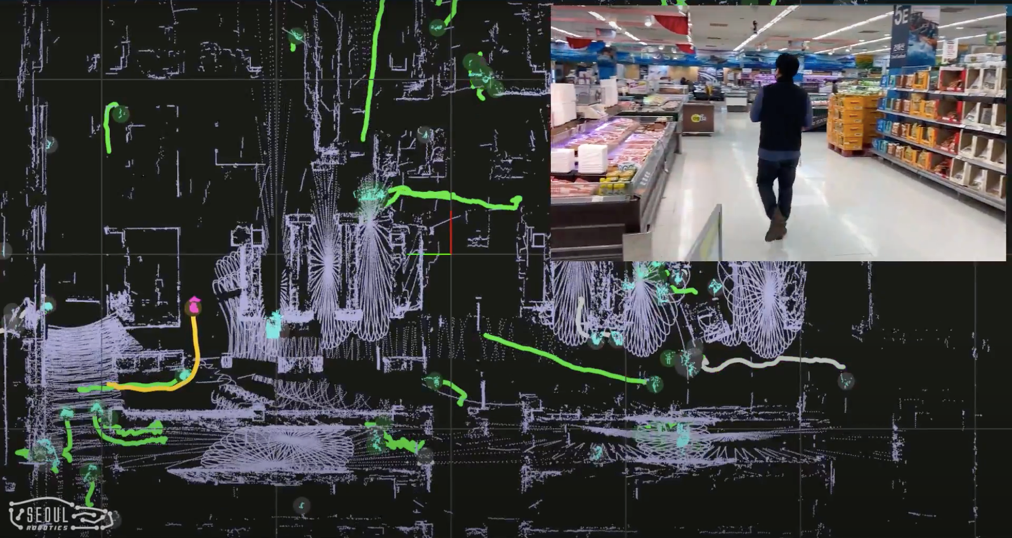

Emart, Korea’s largest retailer, partnered with Seoul Robotics to install patented sensor technology in one of its busiest hypermarkets in the country. In doing so, Emart is able to capture data on customers’ shopping behaviors, such as their typical path around the store and where they spend the most time. Seoul Robotics’ technology also addresses concerns around consumer privacy. By using sensor technology that anonymizes customers rather than cameras that collect their images, no biometric data or personally identifiable information is recorded. This anonymized data is still hugely useful to Emart, though. Through a comprehensive customer data strategy, the information can be used to better manage inventory and product assortment as well as offer customers a highly personalized shopping experience, such as specific coupons based on aisles browsed.
3. Omnichannel 2.0: Bringing Seamlessness Offline
The ubiquity of e-commerce has elevated customers’ all-around expectations of a brand. Consumers have the same demands for ease and convenience when shopping in-store as they do online. Brands should view brick-and-mortar stores as opportunities to weave in technology, create more seamless touchpoints between them and their consumers and offer a true omnichannel experience.

Amazon recently opened its first Amazon Style store, expanding on its offline retail presence portfolio. Amazon Style is the company’s latest foray into fashion and seeks to make in-store shopping as easy and seamless as the online experience. Customers can use the Amazon Shopping app to scan an item’s QR code in-store, which will show them product sizing, colors, ratings and deals. They can then choose to send the item to a fitting room and use touchscreens to request different sizes or colors while also browsing AI-powered recommendations for similar items. Checkout is also a breeze via Amazon One palm scanners: with a wave of the hand, shoppers can purchase their items and be on their way.
But technology alone won’t be enough. Earlier this year, Amazon closed all its Amazon Books and Amazon 4-star retail locations. To fully convince shoppers, Amazon must find a way to create customer-centric experiences that combine the convenience and accessibility of online shopping with the in-store magic that only an IRL experience can deliver.
4. Retail’s Ultimate Edge: Engaging All the Senses
Ultimately, offline retail can win by creating experiences that are simply irreplicable online. Embracing stores as multi-sensorial touchpoints can allow brands to create innovative, memorable and highly engaging customer experiences. Brands that can do this successfully will have no trouble compelling shoppers to move off-screen and in-store.
Scent, one of our strongest senses, has a direct linkage to the part of the brain that controls emotions and memories. When used strategically, scent technology can create a memorable and vivid in-store experience and create desired shopping behaviors. Bloomingdale’s, for example, uses different scents for different sections throughout the store, such as coconut in swimwear and baby powder in infant clothing. Kyobo Book Centre, Korea’s largest bookstore chain, uses a signature scent inspired by trees and wind, meant to relax customers while creating a unified experience across its stores.

Sound plays to another one of our senses and can have a surprising impact on customer behavior, such as increasing brand recall and dwell time by creating a purposeful auditory experience. Genesis, Hyundai’s luxury sub-brand, uses a unique audio identity throughout its entire brand experience, from inside its vehicles to within its showrooms. This auditory expression of its motto, “Quietly Iconic,” is gentle yet distinct, a reflection of the brand’s positioning of modern luxury.
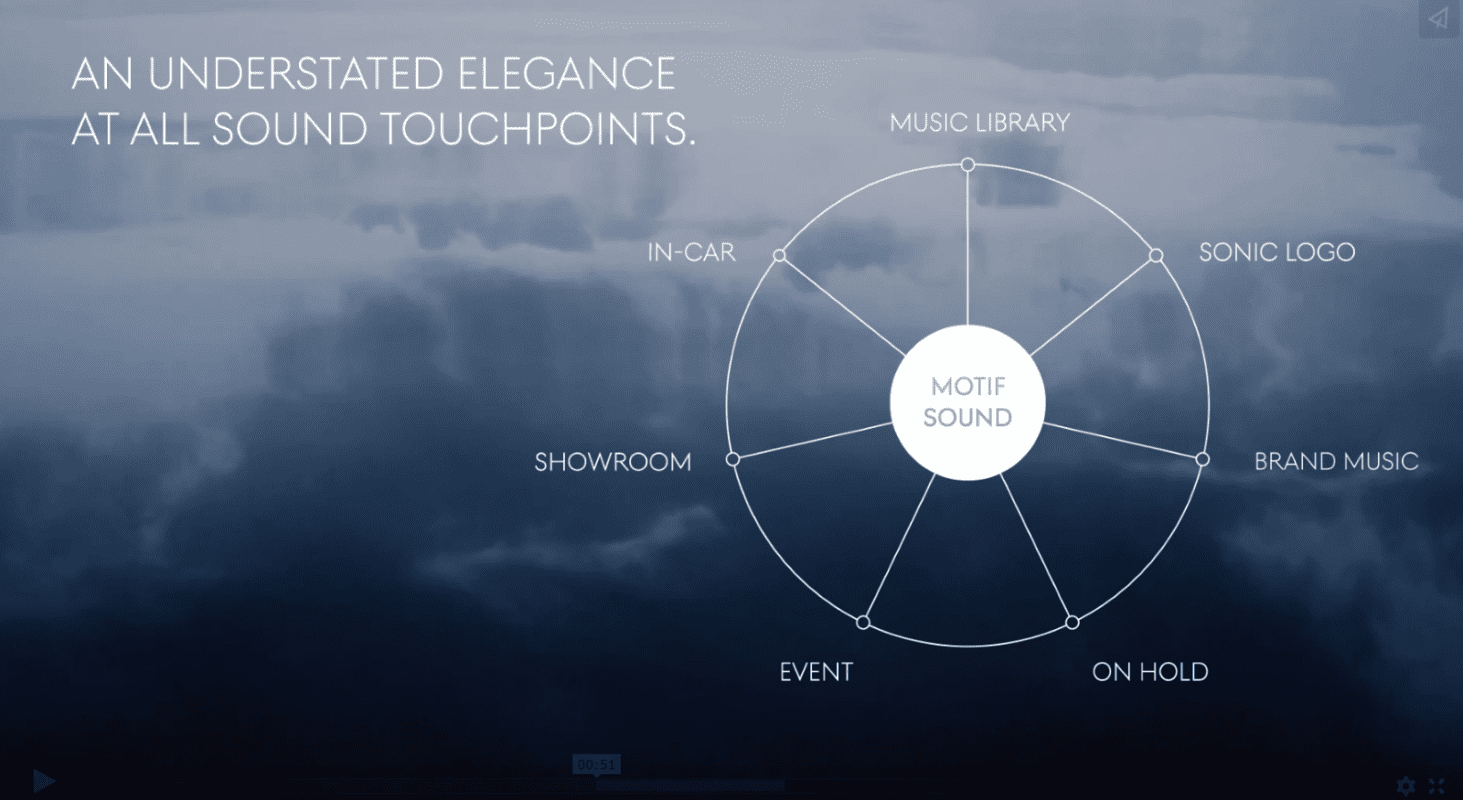
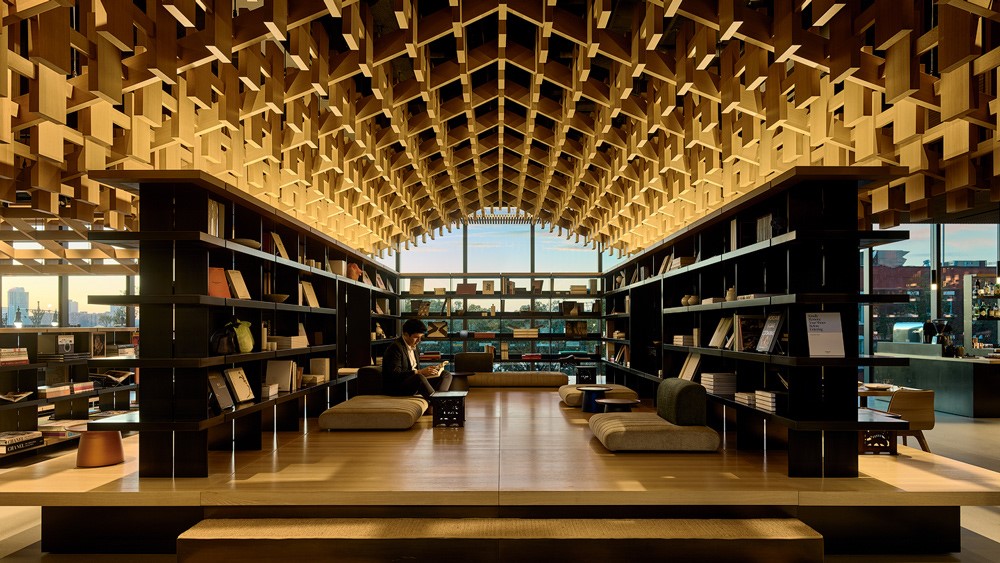
Hyundai recently opened Genesis House in New York, which serves as a brand experience center rather than a traditional showroom, incorporating this meticulously designed sound experience throughout its restaurant, library and event spaces.
FINAL THOUGHTS
While the pandemic posed its fair share of challenges to retailers everywhere, those that have powered through have the opportunity to rethink and redefine their retail experience strategy. Customers are hungry for in-person interactions, and memorable, seamless, multi-sensorial experiences that connect them to the brand – and each other.
Connect with Prophet today to see how we can help reimagine the future of retail for your brand.