BLOG
Future Back Planning: Maximizing Future Growth Opportunities
Future back planning is key to unlocking uncommon growth during times of economic uncertainty.
Future back planning is key to unlocking uncommon growth during times of economic uncertainty.
In our latest global research report, Building Business Resilience Through Innovation, we found that a leading barrier to increasing innovation efforts is that the organization lacks a long-term planning process. Unfortunately for many companies, this has only worsened in the last few years as reactive thinking characterized by the pandemic era.
As innovation leaders emerge from this reactive phase and begin to chart out the next few years of growth during a time of great economic uncertainty, it is essential to create a growth strategy that spans these three-time horizons.
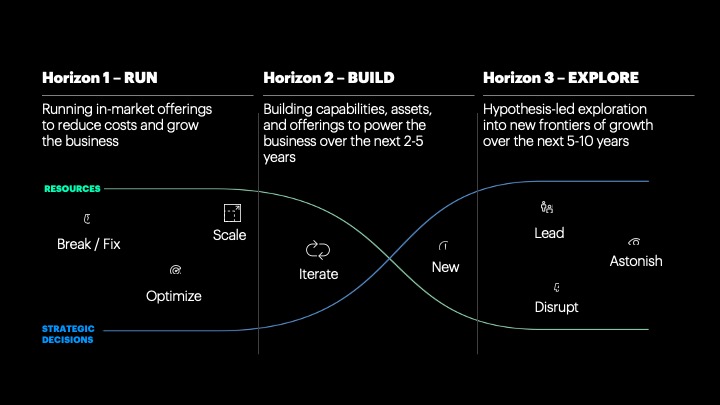
Across these horizons, there is an inverse relationship between the investment in resources and the investment in strategic decisions. Running the business of today is resource intensive and requires operating with excellence with much less space for strategic exploration. In contrast, exploring the business’ target destination over the next five to ten years within a wide open divergence environment is time intensive. Due to the scarcity of resources, it often requires time-bound investment to collect data on the most relevant drivers of change, model potential scenarios that could unfold over time, and based on that, determine what new opportunities are worth further validation and investment.
In Horizon 1, the existing value chain is used to optimize and scale the business, but in Horizon 3, the needed value chain will most likely be adjacent to today’s value chain. The inversion point of building the new value chain is challenging to manage because resources are ramping up as the ability to make strategic decisions is fading. At this point, the skills required to be successful change. It is operationally complex to get something to move through the inversion curve.
If a business neglects Horizon 3 activities today, it sets itself up to be leapfrogged by the competition because it will not have invested in the assets and capabilities needed to act on emerging opportunities.
Future Back Helps Companies Maximize Growth Opportunities in Horizon 3
While it is impossible to predict the future, market leaders and makers proactively anticipate preferred and disruptive future scenarios. The first step is understanding the most impactful drivers of change that will shape the future market landscape. Drivers of change come from a range of sources: the classic Porter’s Five Forces of suppliers, buyers, new entrants, substitutes and competitors that determine industry profitability, as well as macro-forces that are broader than industry boundaries, often categorized as social, technological, economic, environmental, and regulatory drivers (STEER).
From doing future back work across industries, we have found three non-mutually exclusive factors that help us see around corners. Across these factors, emerging technology is critical in reshaping societal norms, enabling new interaction modes, and determining future profitability and competitive advantage sources.
3 Non-MECE Factors that Shape the Future Market Landscape
1. The Overton Window describes the range of policies that are accepted by the mainstream at a given time and can be used to identify ideas on the threshold of gaining mainstream acceptance. For example, over the last 50 years, public acceptance of in-vitro fertilization (IVF) has rapidly increased as the availability of IVF technology has also grown. In 2021, fertility support startups raised $345M, up 35% from the previous year. Health systems and payors that anticipated this shift ten years ago were able to differentiate themselves within a rapidly growing market. However, with the overturning of Roe v. Wade, societal progress regarding IVF is now under threat. Industries heavily funded by the government, such as healthcare and clean energy, are also strongly shaped by changing societal norms.
2. Behavioral shifts often emerge due to technological advancements that make it easier to do more with less or create new modes of interaction between humans and machines. For example, Figma’s significant innovation was being browser-first, with the ability to edit files in real-time in the cloud, allowing teams of developers, designers, and product managers to collaborate in one place efficiently.
Adobe was late to the game of browser-first collaboration and, as a result, paid $20 billion to acquire Figma, which had roughly $400M in revenues at the time. The steep price was considered a solid investment given the future value of Figma’s product spaces. Thinking more broadly, technological advancements across the Internet of Things, artificial intelligence, artificial and virtual reality, and autonomous machines will enormously impact behavior and interaction modes, changing how we learn, work, collaborate and entertain ourselves.
3. Business model shifts are often required to capitalize on or meet emerging technology demands, regulation, the economic environment, and ESG agendas. For example, Fundrise was the first company to crowdfund real estate investment successfully, and the founders did it by seeking the expertise of regulators from the beginning. Working with a former regulator, Ben Miller figured out how to use Regulation A to raise money from non-accredited investors, which was the first time anyone had ever done. Eventually, the regulation changed to Regulation A+, which allowed the company to raise more equity from non-accredited investors while streamlining the filing process. Still, at that point, Fundrise was already the category leader in a new market.
Four Questions to Determine a Company’s Options within the Future Market Landscape
Once we understand the most impactful drivers of change, the next step is modeling the most viable opportunities for a specific company to pursue. We begin with four questions:
1. How is a company encumbered and advantaged?
This includes understanding a company’s options based on its funding and regulatory moats. Firms funded by unregulated capital have an entirely different set of options than firms funded by regulated capital. A venture capital-funded firm can take on much higher fixed costs to stand up a new capability without a near-term path to profitability. For example, the data cloud company Snowflake raised $2.1B over eleven rounds of funding since 2012 and isn’t expected to reach profitability until 2023.
On the other hand, an advantage of being a large, publicly traded company is that it is easier to find suppliers and partners to test and validate Horizon 3 growth hypotheses with and bring new offerings to market. Along with understanding the implications of funding sources, it’s essential to know where margins come from today – is it from hardware, software, or services? Who has the most power in the value chain to extract more margin over time? What parts of a company’s existing product line, assets, and capabilities might serve as a moat? Does it have access to a rare resource on the supply side or a lock-in effect on the consumer side? Finally, is there a regulatory moat that will make it difficult to unseat an incumbent?
2. Who has the preferred position in the market to launch and scale this idea?
The most critical mindset of future back work is humility. We always assume that another player is better set up to execute an idea. The big four (Alphabet/Google, Amazon, Apple, Meta/ Facebook) dominate their innovation ecosystems due to their scale, network effects, and ability to buy entire markets. Firms operating within these ecosystems are often unlikely to win share-of-wallet among end consumers and are much more likely to succeed by playing a critical infrastructure or support role. We look at the role of aggregators and integrators in the innovation ecosystem to understand how parts of the market are consolidating and where technology is being abstracted away from the end user.
3. Who is the player that can shut this idea down?
As Archimedes said, “The shortest distance between two points is a straight line.” In highly regulated industries such as financial services and healthcare, a significant source of Horizon 3 growth is creating new business models based on the changing regulatory landscape. Like the Fundrise example, the founder of Coinbase realized that abiding by U.S. law rather than moving offshore could act as a long-term defendable moat for the company. With the collapse of FTX, that bet has already paid off.
4. What has prevented this idea from being launched and adopted before?
Is the idea on the threshold of becoming mainstream? Is there a consumer experience problem or a price-to-value problem? Or does capital not think it’s worth an investment? The inevitable endpoint of markets is to solve consumer problems rather than business and technical problems. Enterprise capital is good at solving Horizon 1 business problems, such as increasing conversion in existing channels, creating efficiencies, and increasing margins.
On the other hand, venture capital is good at investing in long-plays that create new consumer markets because it has a risk appetite and is willing to be too early. Too early might mean taking on the cost of educating the market about a problem that they should have realized could be solved. For example, Netflix was loved for eliminating late fees (a consumer problem previously considered unavoidable in a physical rental market). Still, the company was perceived as shifting to a digital-first business model too quickly. Success in bridging the gap between its Horizon 3 digital-first business and its Horizon 1 DVD rental business required subsidizing the price of the new service for end consumers.
The Mindset We Bring to Future Back Work
The future back process combines design methodology (outside-in and hypothesis-led) with business rigor (commercial opportunity assessment with an asset-forward view of value-chain adjacencies and potential competitive moats).
The mindset we apply to this work draws from design and consulting. We’ve distilled it into three design principles:
Humble
We begin this work by assuming that another player has a better solution as well as a preferred position in the market.
Anti-fragile
We create a durable portfolio of growth moves in order to hedge our bets, with the understanding that it is impossible to know exactly how the market will reshape over time.
Effective collaboration
You need to keep running the business of today while exploring what your business might be in the future. At the same time, your hypotheses around how the market might shift and what options are most attractive for your company are the entry point into this work. We design future back engagements to extract maximum input in the most time-efficient way by starting with stakeholder hypotheses, bringing in external experts to identify new opportunities and threats quickly, and then designing workshops and executive communications that bring your team along the right way at the right time.
The Outcomes We Achieve Through Future Back Work
There are three main outcomes that we have consistently achieved through this work:
- Board-level alignment and buy-in on a future vision. For example, supporting the approval of a board-level, multi-hundred-million-dollar M&A strategy in order to create an entirely new product category.
- Driving capital allocation for new business building. For example, on a recent project, this work led to a $5 billion acquisition as the centerpiece of a new business unit.
- Updating the product roadmap to transition from now and near-term investments to decisions that will drive the next horizon of the business.
FINAL THOUGHTS
We would love to do this work with you. If you already have hypotheses on the future of your business, we can dive into a Future Back project to explore, validate, design and quantify those opportunities. If you know that your company needs a Horizon 3 growth strategy, but your leadership team isn’t bought in, we have interim steps to drive alignment among stakeholders while collecting initial hypotheses on potential sources of long-term growth.
Interested in maximizing your future growth opportunities? Please get in touch.

