BLOG
5 Archetypes of Digital Business Models
One of the most effective ways to achieve uncommon growth is through business model innovation. For digital business models, this requires creating a revenue model that is in service of your value proposition.
If you look at your phone’s home screen, you will see many digital business models in the form of frequently used apps: Uber, LinkedIn, Teams and Spotify to name a few. Each of these companies has a native digital business model in contrast to non-native digital companies that use digital as a sales channel (e.g., Walmart). In this article, we dive into the five archetypes of digital business models with examples to show the tradeoff decisions and investments required to be successful in each archetype.
At Prophet, we define a business model as how a company creates, delivers and captures value with five main components:
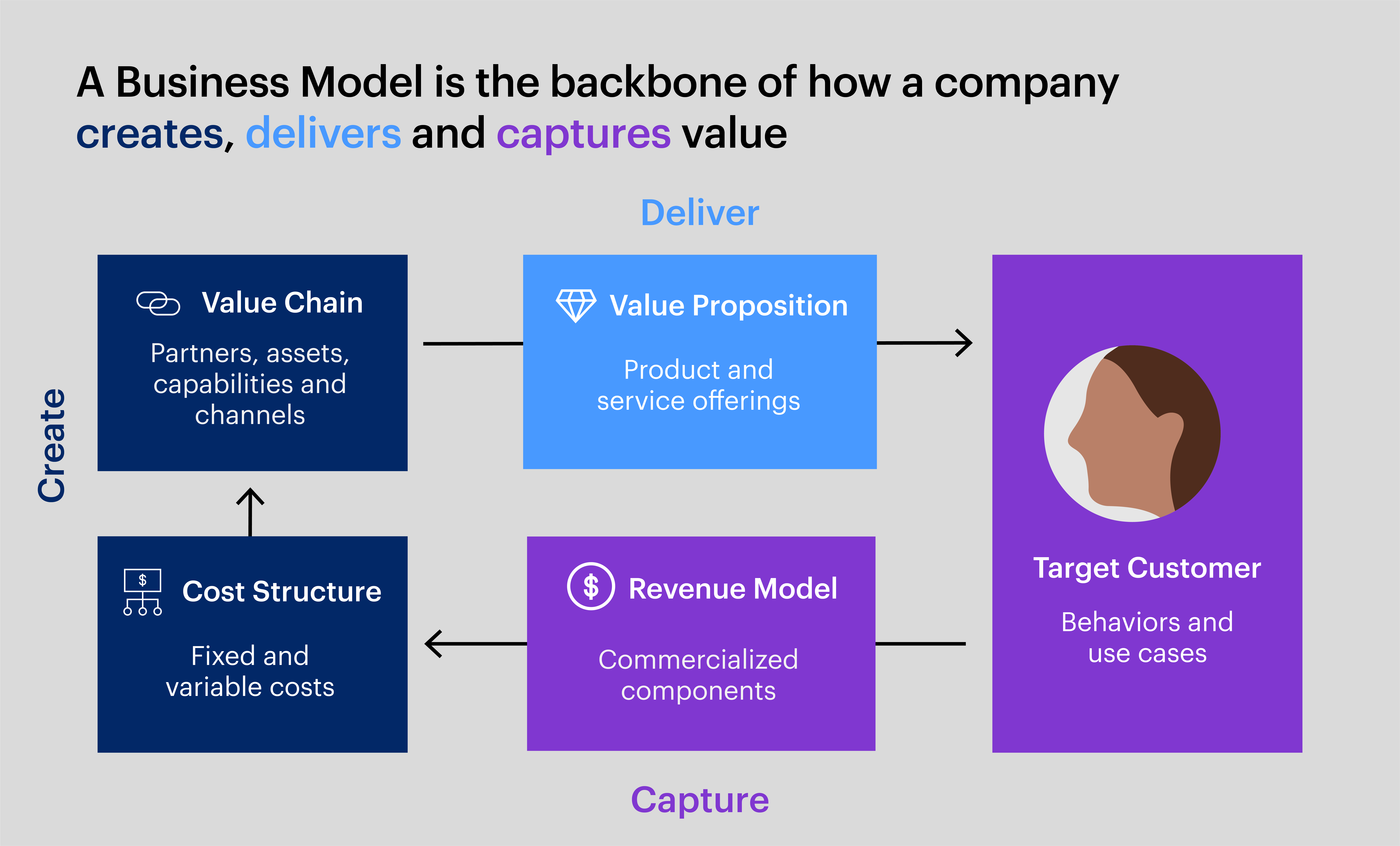
Two components of this model can be used to deconstruct the five archetypes of digital business models: (1) the value proposition, what you offer in the form of products and services and (2) the revenue model, how you commercialize those offerings.
Digital Business Model Decision Tree
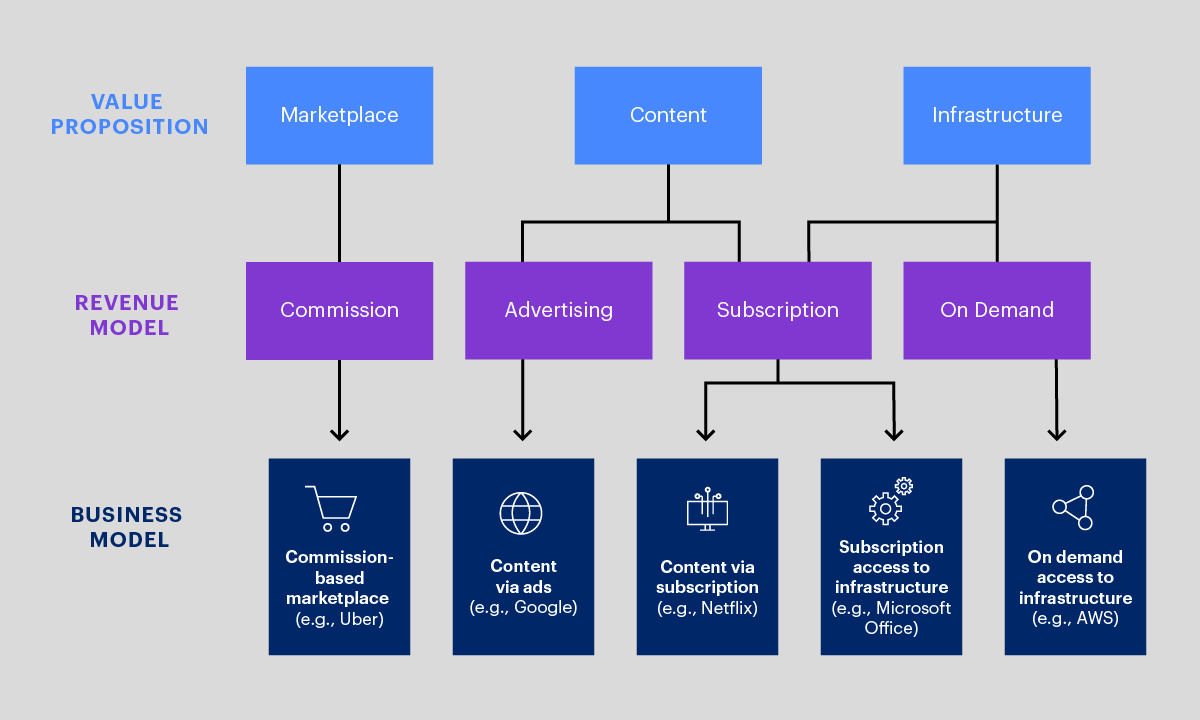
Value Proposition
The first decision when designing a digital business model is how you will create value. Will you own your own supply or aggregate third-party suppliers? Marketplaces connect suppliers with buyers for products and services. Content providers create or aggregate content that can be read, listened to or watched. Infrastructure providers’ own enablers needed to get things done.
Revenue Model
The next decision is how you will monetize your offering. Will it be paid for by end users or by a third party? Marketplaces are primarily monetized through transaction fees charged to both suppliers and buyers. In addition, marketplaces can charge suppliers to advertise or offer their users subscriptions to reduce transaction fees. For content providers, the decision to monetize through advertising versus subscription depends on scale. An advertising model reduces costs on end users, enabling scale and network effects. A subscription model provides more predictable revenue from each user and locks in revenue for longer cycles. For infrastructure providers, an on-demand model can provide a cost-based competitive advantage but requires a huge investment in upfront costs. Infrastructure as a subscription provides more funding for ongoing product development and innovation.
An Example of Each Digital Business Model:
1. Commission-based Marketplace (e.g., Uber)
In this business model, suppliers and advertisers pay to access customers in a marketplace. The main revenue drivers are transaction fees, listing fees and advertising. This business model requires creating a flywheel between multiple parties. Uber’s business model includes a DTC service and separately a B2B and B2D (business to driver/courier/biker) marketplace. In Winning Through Platforms, Prophet Senior Partner, Ted Moser describes the advantage Uber gained through creating a unique “customer coalition edge” among multiple parties: riders and delivery recipients, ride and delivery drivers, app developers, advertisers, restaurants and regulatory bodies. By bringing together such a robust customer coalition, Uber can provide more value to each customer group, while also diversifying their revenue sources and differentiating from competitors. Uber attracts more drivers than Lyft by offering revenue from rides, deliveries and in-car advertising. By attracting more drivers, Uber can also attract more riders to their platform with greater ride availability. That, in turn, has the flywheel effect of bringing on more suppliers – including advertisers, developers and restaurants. As a result of these moves, Uber commands a 20x higher valuation than Lyft today at $128B.
2. Content via ads (e.g., Google)
Back in 1999, Google’s founders considered two ways of monetizing: subscription and advertising. The subscription model they considered was $20 a year paid by the end user. For that same user, the advertising market would value them at an average of $52 per year in 1999, so 2.5x more. A Wharton paper found that platforms monetized via advertising versus subscription are more likely to invest in content moderation to expand the user base to large, heterogeneous populations. A central tension in the ad-supported business model is that polarizing content is good at getting attention, but over time, it can lead users to be less satisfied and engage less. In addition, advertisers require a high level of stability to ensure that their ads do not appear next to harmful content.
3. Content via Subscription (e.g., Netflix)
Platforms with a subscription model must balance growth alongside increasing the willingness of the user base to pay. There is fierce competition for recurring revenue, so subscription players must continue to increase the value that they provide to end users each month. For Netflix, it became difficult to continue to show growth once almost everyone in the U.S. had access to a Netflix log-in through their family and friends. In November 2022, Netflix launched a new ad-supported tier, and a few months later, Netflix began cracking down on password sharing outside of households to force new customers into the ad-supported tier. Netflix also raised the price of the non-ad-supported tier, which forced customers to choose between paying more each month or allowing Netflix to monetize their viewing with advertisers. These moves caused Netflix to have its strongest quarterly increase in customer gains in three years.
A note that these first three business models all fit into Ben Thompson’s definition of Aggregators: companies that have a direct relationship with users, zero marginal cost for serving those users, and decreasing acquisition cost as the user base grows. This theory explains how platforms have radically reshaped industries by making control of demand much more important than control of supply. For example, Uber has been much more successful than taxi services by focusing on the end-user relationship rather than trying to control the supply of drivers. In the digital world, attention is a scarce commodity rather than a finite resource, so it is much more important to own the end-user relationship than it is to own the supply.
4. Subscription Access to Infrastructure (e.g., Microsoft Office).
In this business model, customers pay per seat to access a service. This provides monthly or annual recurring revenue in the form of licensing fees. It is a capital-intensive model that requires ongoing investment in product maintenance as well as product development to retain and acquire new customers. Microsoft recently debuted Copilot, an AI-enabled enhancement to the suite of Office products to differentiate itself from workplace software competitors such as Google. Another form of competitive differentiation is being the one-stop shop for everything. Microsoft is essentially the operating system of work, with all the necessary applications and services – from communication to email to productivity and presentation tools, in one place and connected to each other. Microsoft does not have to have the best single product for anything, for example, many employees prefer Slack to Teams, but by integrating everything in the cloud, the switching costs are too high to opt out of Microsoft’s ecosystem for a single app.
5. On-Demand Access to Infrastructure (e.g., Amazon Web Services)
This business model requires significant upfront fixed costs to have capacity available on demand. One of the most in-demand types of digital infrastructure today is Nvidia’s H100 AI chips, which are used to power ChatGPT and other AI apps. Crusoe Energy, a digital infrastructure provider, raised $200M to buy these chips and is forecasted to make half of that investment back in just one year by charging companies for access. The biggest incumbent in the digital infrastructure model is Amazon Web Services, which Jeff Bezos has likened to the utility companies of the early 1900s. Back then, factories had to build their own power plants to generate electricity, but once the factories could buy electricity from a public utility, they no longer needed to invest in expensive private electric plants. In this analogy, electric plants are physical computing technology. By providing servers and storage in the cloud, companies can reduce their fixed investment in computing and storage and pay for what they use, and when they need to use more, it is easy to scale up the capacity. Today, the cloud platform industry is valued at $180B, with AWS controlling a third of the market. In addition, AWS is responsible for about three-quarters of Amazon’s total operating profits.
Overview of revenue attractiveness and investment required for each business model:
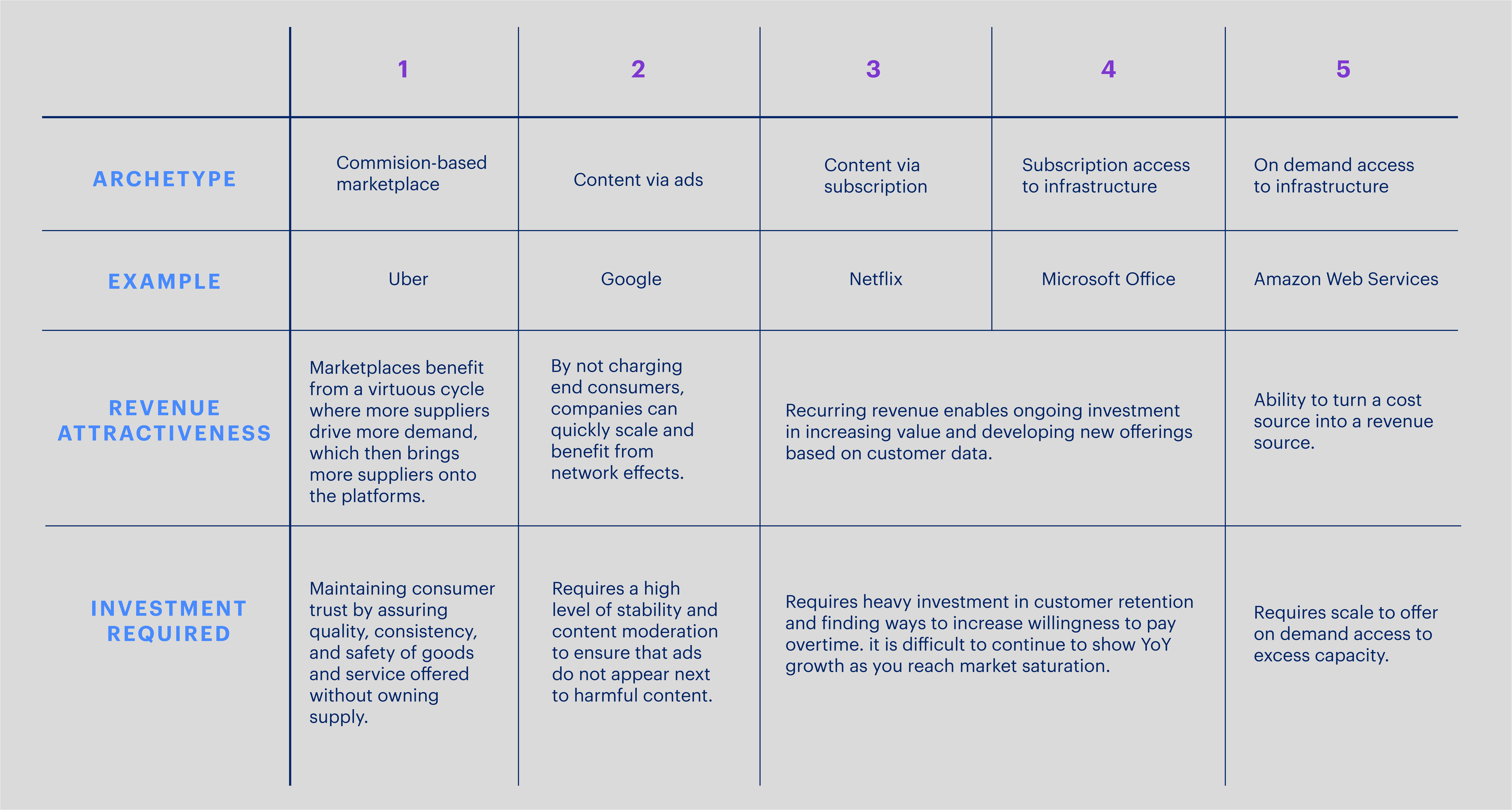
These are just a few examples of companies that fit into the five digital business model archetypes. We have partnered with a number of clients to design and launch new business models as well as to innovate existing business models in the face of change.
Creating a new Digital Business Model:
- We helped a hardware manufacturer create a new on-demand access to infrastructure business model by embedding smart home technology into their physical products, enabling our client to become an essential infrastructure and service provider for home security players.
- We worked with a healthcare association to transform its business model from membership fees to a new digital learning platform that prepares healthcare workers for the jobs of the future.
Evolving a Digital Business Model:
- We partnered with a content provider to quantify the impact of transitioning from a subscription-only model to an ad-supported model.
- We worked with a telecommunication provider to pivot from a usage-based model to a monthly subscription.
FINAL THOUGHTS
Contact us to learn how to partner with us on developing, quantifying and launching a new or evolved digital business model to drive business growth.

