BLOG
Deepen Innovation Maturity to Win Out Fintech Disruption in Southeast Asia
How financial services companies should innovate in this disruptive landscape in SEA.
Financial services companies are at a crossroads, facing an unprecedented risk of relinquishing their dominance. The unique financial services landscape in Southeast Asia (SEA) has paved the way for disruptive fintech companies to emerge as agile and visionary players, causing significant disruptions in the sector. To stay ahead of the game, traditional and international banks must enhance their innovation capabilities and embrace a progressive mindset as business models have changed and more disruptive fintech companies establish themselves in the industry.
The Unique Financial Services Market in Southeast Asia
One of SEA’s unique characteristics lies in its strong demand for convenient and accessible financial services, driven by a relatively large underbanked population. The Global Fintech Report estimates that over 70% of the Southeast Asian population remains unbanked or underbanked, with Vietnam, the Philippines and Indonesia having the highest combined rates. Coupled with a large population of young and digitally savvy consumers, SEA’s digital economy has enormous growth potential. It is also worth noting that micro, small and medium enterprises (MSMEs) are huge driving forces of the SEA economy but most of them face difficulty in securing bank loans as they are unable to meet the eligibility criteria.
Moreover, the regulatory environment in SEA has made the region a fertile ground for fintech innovation. Singapore, Vietnam and Indonesia are now dominant players in the regional fintech scene, establishing a supportive regulatory environment that has driven the rise of virtual banks and encourages innovation and collaboration between fintech startups and traditional financial institutions.
The uneven financial services landscape in SEA has given birth to virtual banks and led digital native startups to venture into developing accessible and inclusive financial solutions for underserved populations in the region. With a strong culture of innovation, fintech companies and neo-banks in the region have been able to reach the underserved micro-segments that incumbent banks were unable to fulfill.
A Dynamic Landscape of Fintech Disruptors
Among the disruptors, Chinese powerhouses Ant Financial and Tencent have emerged as formidable players, shaking up the local financial services scene by introducing e-payment solutions for tourists and partnering with local players. For instance, Ant Financial has invested in Ascend Money in Thailand, and Mynt in the Philippines, while WeChat Pay partnered with PT Bank CIMB Niaga Tbk to enter the Indonesian market. These disruptive business models in China have influenced SEA markets to accelerate innovation. Agile players like Singapore’s Grab and Indonesia’s Gojek have since expanded into the financial products, digital payment and e-wallet ecosystem. Each country has witnessed the rise of strong fintech players providing e-wallet services – Momo in Vietnam, PayMongo in the Philippines, Boost in Malaysia, GoPay and OVO in Indonesia, and GrabPay in Singapore. Not to be outdone, telecommunication companies are now diving headfirst into the fintech realm, forging strategic partnerships to expand their offerings far beyond their traditional core services.
Furthermore, we are seeing increasing collaboration between incumbent banks and fintech companies in the region. For example, Siam Commercial Bank’s fintech subsidiary, SCBX, has announced its readiness to apply for a virtual banking license in partnership with South Korea’s largest digital bank, KakaoBank. By offering digital banking services in Thailand, SCBX aims to enhance competition and address the challenges faced by underserved individuals in the country. Similar collaborations have occurred in Singapore and Malaysia, where joint ventures between super apps like Grab and telco brands like SingTel have given rise to virtual digital banks. Notably, AirAsia’s fintech unit BigPay and Malaysian telco giant Axiata have also partnered with lender RHB Group to drive innovation in the financial services sector.
As such, the ongoing fintech revolution in SEA is transforming the way financial services are provided and consumed, bringing financial inclusion and innovation to the forefront.
Rising Challenge for Traditional Banks
With dynamic fintech companies being laser-focused on addressing the needs of underserved segments, fintech’s impact in SEA is undeniable, pressurizing incumbent banks to innovate and transform.
Several traditional banks have demonstrated a strong capacity to withstand fintech incursions and even turn the tide in their favor. An example is MB Bank, one of the largest financial groups in Vietnam that embarked on a digital transformation journey in partnership with Prophet. Through a customer-centric digital transformation and a new innovative growth hack business model, MB Bank successfully reimagined its business, products and experiences, acquiring some 20 million new customers in just 3 years with its new tech-like banking platform unlike any in the region. Gaining leadership as the No.1 digital bank and recognized as the most valuable brand in Vietnam by Brand Finance, MB Bank is now proudly listed as one of The Forbes Global 2000 list of the world’s largest firms.
MB Bank’s remarkable disruption of legacy banking and admirable achievements serve as an inspiration for other traditional financial institutions seeking continued success in the digital era.
Leveraging the Innovation Maturity Model for Traditional Financial Services
To help financial services companies rethink and review their innovation strategies, Prophet’s financial services experts developed the Innovation Maturity Model to offer a definitive roadmap for organizations to outperform disruptive fintech firms. The model provides a systematic blueprint, with a focus on essential pillars such as strategy, organization, insights, culture, and education, to ensure effective performance. By leveraging these pillars, organizations can make well-informed strategic decisions and cultivate a culture driven by innovation, empowering them to seize growth opportunities.
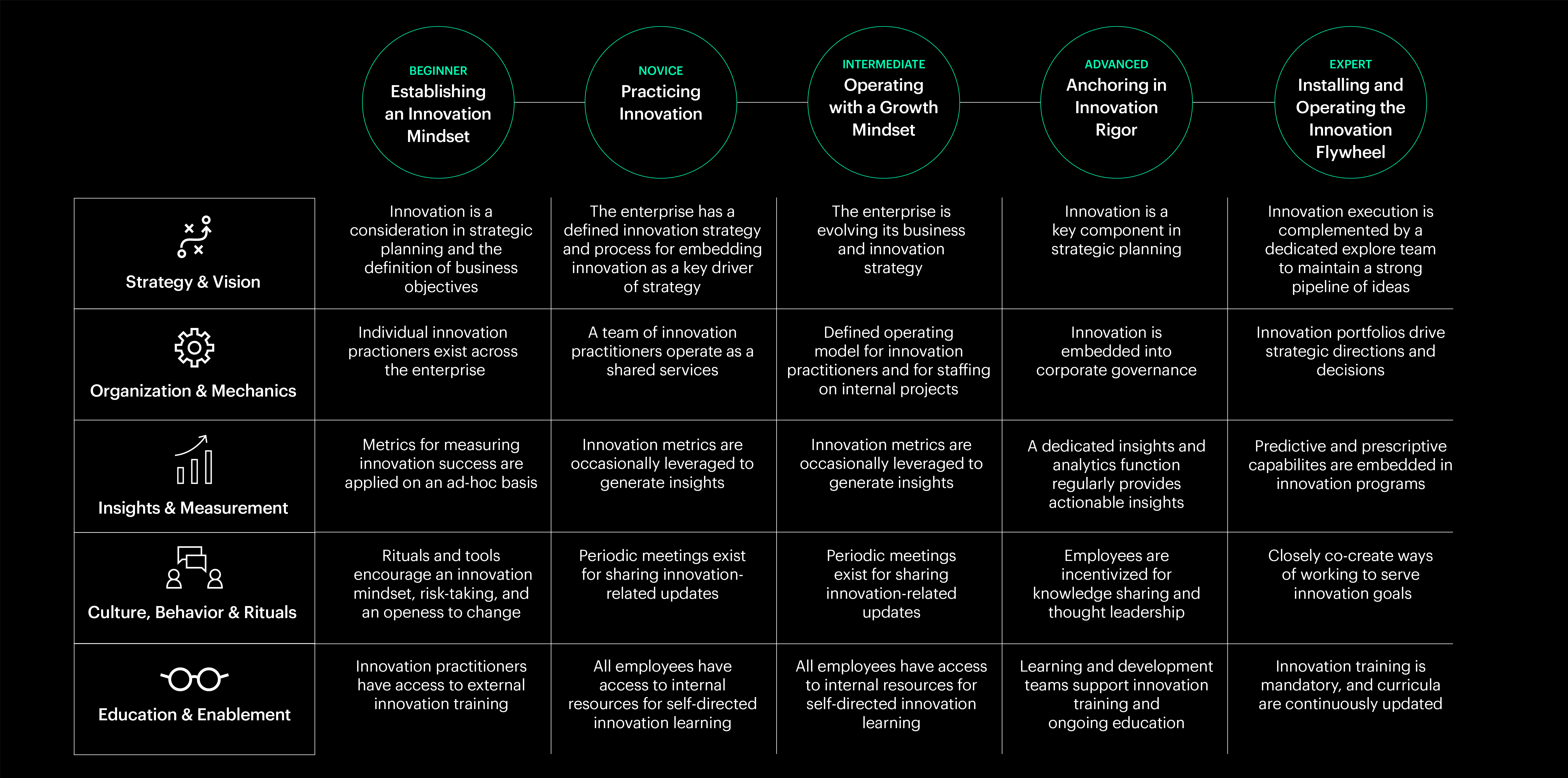
Importantly, traditional financial services companies must foster a culture of disciplined and rigorous innovation to gain an edge over the pervasive threat posed by fintech disruptors. The five pillars of the Innovation Maturity Model offer guidance and ammunition. By adopting this model, companies are able to inspect five dimensions of the business that are critical to enabling innovation.
1. Strategy and Vision
The key to successful innovations lies in a focused strategy that aligns closely with customer truths and relevance. By developing future-proof solutions rooted in a profound understanding of current and future customer needs, financial services companies can navigate the dynamic industry landscape and remain competitive in the long run.
Take inspiration from MB Bank, which gained a deep understanding of the pain points faced by Vietnamese consumers when it comes to banking. It had thus defined a clear strategic vision for its transformation to be a customer-centric and digital-first bank of the future, unlocking a series of innovative digital experiences for its young and underbanked audience.
2. Organization and Mechanics
It is crucial to embed innovation throughout the organization to efficiently deliver cutting-edge products and services. This involves fostering internal collaboration across different functions and tapping on external perspectives and knowledge, including that of fintech companies.
A notable example is Standard Chartered’s collaboration on Mox (in partnership with HKT, PCCW and Trip.com) and Trust Bank (collaboration with Singapore’s leading retailer Fairprice), which enabled them to leverage the latter’s advanced huge customer base, technological infrastructures and cloud-native features. The consequential improvements in Standard Chartered’s operational efficiency and customer experience highlight the advantages of collaboration even with unexpected partners in the financial sector.
3. Insights and Measurements
To stay attuned to customer expectations, financial services companies must facilitate the integration of predictive and prescriptive capabilities. By harnessing the power of data analysis and insights, financial services companies can anticipate future needs and make informed decisions.
MB Bank for example greatly stepped up its data analytics with its enterprise transformation, boosting insights with real-time dashboards across critical customer touchpoints as well as investing in Martech to better understand customers and improve customer experiences.
It is imperative for financial services companies to consistently monitor the relevance and effectiveness of their initiatives and be receptive to necessary changes. By doing so, they can react faster and sharper to ensure that their innovation and customer experience initiatives remain in sync with customer expectations, resolve pain points and stay ahead of the curve.
4. Culture, Behaviour and Rituals
Fostering an innovative culture is also pivotal to achieving long-term success. Financial organizations must adopt a mindset of perpetual learning and refrain from assuming that past practices alone will be adequate in the future. This is especially so as fintech and Insurtech are two of the fastest growing in SEA where innovation is the bedrock of these disruptors.
Apart from inculcating an innovation culture with ongoing initiatives, activities like hackathons widely used in tech firms are also effective approaches to fostering innovation as they promote learning, skill development and exposure to novel methodologies and ideas. Hackathons can also serve as powerful recruitment tools. DBS, for instance, strategically leverages programs like Hack2hire to identify and attract highly skilled individuals with expertise in cloud technologies, AI, Big Data, and analytics. By hosting such hackathons, DBS creates opportunities to engage with talented individuals and recruit them into their organization, ensuring a pipeline of top-notch talent in relevant domains.
MB Bank’s HIVE innovation lab is another notable example where new ideas are incubated, with collaborations with start-ups, and internal growth hacks and product innovations are continuously tested and piloted.
5. Education and Enablement
Financial services companies must also recognize the importance of education and enablement. Traditional providers should strike a balance between internal and external education, offering training and enablement programs to keep employees updated on emerging trends and agile solution-building.
Both DBS and MB Bank exemplify dedication to continuous employee development through the establishment of DBS Academy and MB Academy respectively. Through a blend of formal training with communities-based learning, both banks aim to equip their workforce with the necessary tools and digital skills to thrive in dynamic business environments.
Additionally, establishing strategic partnerships and providing educational content to ecosystem partners empowers them with the latest technological developments.
FINAL THOUGHTS
In this heavily fragmented and competitive financial services market, international banks and local giants confront the need to evaluate their capacity to effectively participate and thrive in local markets. Prophet’s Innovation Maturity Model presents a proven transformative framework that empowers financial services companies to bolster their innovation capabilities to drive sustainable, uncommon growth in the constantly evolving financial landscape. We’d be delighted to speak with you regarding your firm’s innovation outlook and how we can help you achieve them.


