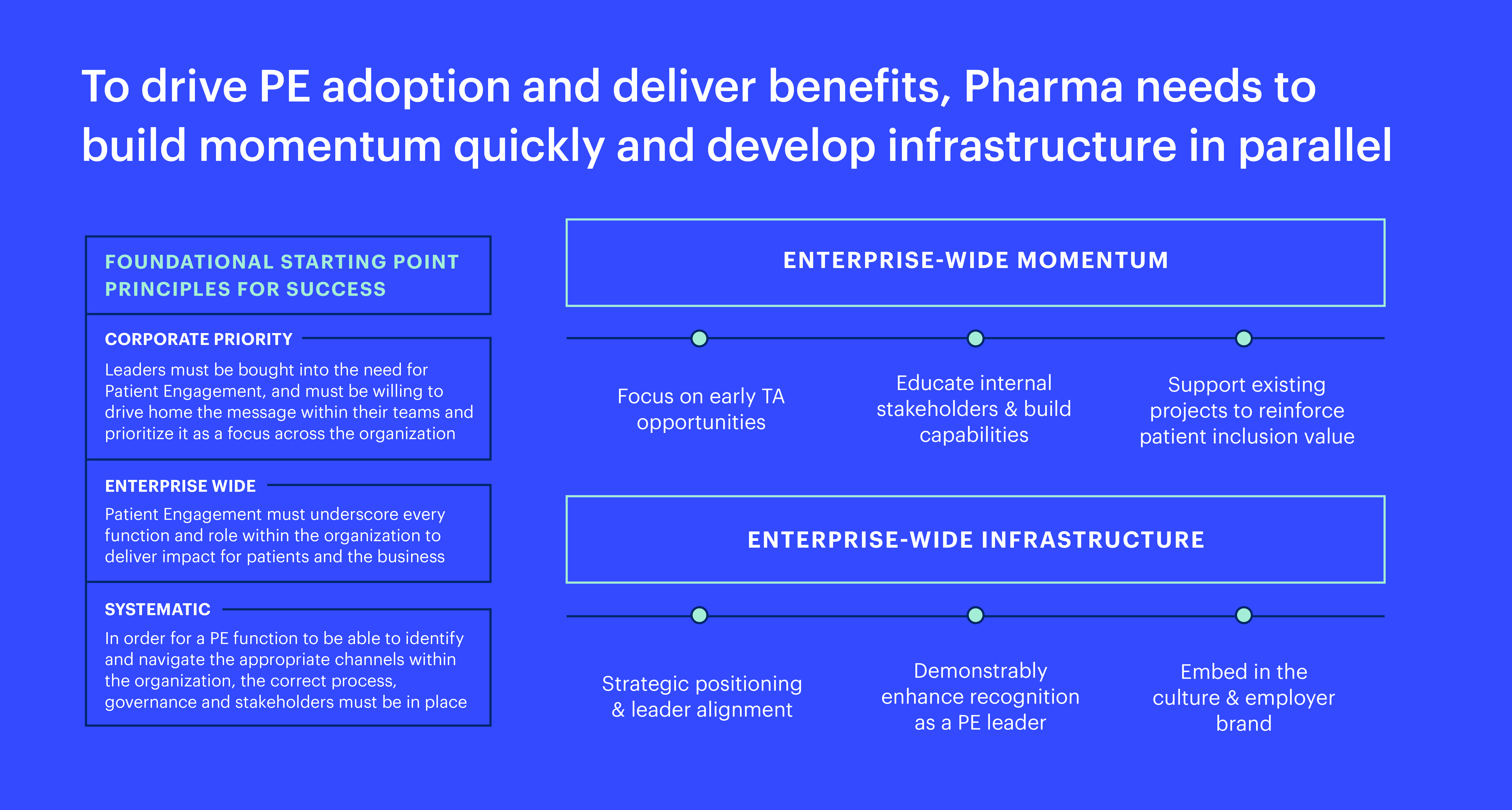
BLOG
Five Healthcare Trends To Watch in 2023
Healthcare leaders can drive change in 2023 by thinking boldly and targeting investments in the following trending healthcare spaces.
Looking ahead to 2023 in healthcare, the big macroeconomic clouds on the horizon make for a less than cheery outlook. The combination of an economic downturn and higher costs will be a dominant theme for the entire healthcare industry and a huge challenge for organizations across hospitals, health systems and device makers, pharmaceuticals, and life sciences companies, as well as players in technology.
Still, taking the glass-half-full view, we see many opportunities for leaders across the business to drive operational discipline and innovation by focusing on investments that matter most in driving better outcomes for all stakeholders. As we point out in our transformation playbook, changemakers that push beyond the many common barriers to innovation can achieve a great deal. Yes, the economic pressures will be greater. But 2023 will see plenty more disruption – and thus plenty of growth opportunities – as our annual list of healthcare trends below makes clear.
1. Holistic Wellness Solutions Continue to Influence the Market
Successful one-off wellness apps and small niche solutions are adopted by large employers and payers to enhance benefits programs and give people more options to live healthier lives. As consumers adopt wearable data trackers in support of that goal, they will increasingly choose to work with healthcare organizations that are committed to holistic wellness.
It’s not about the gadgetry, but rather driving good outcomes, particularly relative to social determinants of health (SDoH) and patients’ lived experiences. The start-ups and tech firms with the most attractive and powerful solutions will achieve rapid scale by going the B2B2C route. We think the biggest winners will emerge in in-home diagnostics, preventative health opportunities (e.g., perimenopausal women and metabolism and nutrition) and mental health, which will be of interest to large employers, as well as individuals. Apps and widgets that empower individuals with their own data, plus timely prompts and attractive incentives, will crack the code on growth.
2. Venture Capital Focuses on the Best and Brightest
While we expect to see a few big winners among tech players, most firms will face a tighter funding landscape and more intense due diligence. Venture capital, which has been flowing freely and voluminously for years, will become less available as investors scrutinize business models more closely and back only the best and brightest.
We suspect the firms that attract funding will be those that focus on narrowly defined patient cohorts already engaged in self-monitoring behaviors and where innovation can move the needle on cost control or value delivery. Those that can collect real-world data from outside the four corners of traditional clinical environments, and integrate seamlessly into core systems, will be specially well positioned to attract funding and potential partners. Chronic disease management, patient engagement and population health solutions will also be priorities because there is clear clinical and financial upside in all these areas.
3. The Workforce Shortage Worsens as a Full-Blown Crisis
With continuing burnout among healthcare workers, large provider organizations face issues with care quality and deteriorating patient experiences. The supply-demand fundamentals are inescapable: There are simply not enough doctors, nurses and paraprofessionals – not to mention data scientists, business analysts and experience designers – to fill all the vacancies.
However, there are multiple potential solutions to resolving talent shortfalls. Workforce optimization and workflow efficiency are necessary, so too automation and more advanced technology in everything from reading x-rays to identifying payment fraud. More support for patient self-monitoring, continued expansion of telehealth and in-home care will also help alleviate chronic talent shortages. There’s also a large cohort of tech-savvy talent looking for jobs with a higher mission after layoffs from Silicon Valley giants.
4. Value-Based Care Models Become Innovation Labs
The inevitable momentum toward value-based continues. More than 40% of U.S. healthcare reimbursement now has some value-based component, a proportion that will only rise in 2023 and beyond. Though pockets of resistance remain, more provider organizations will advance and mature their Value-Based Care capabilities. And they’ll do so on several fronts. More sustained preventative outreach efforts to underserved, high-risk and high-cost populations for routine screenings will continue producing strong results. Shared-incentive contracting will be more attractive for capital-intensive equipment, such as MRI machines and CT scanners.
Sophisticated technology usage will be a hallmark of VBC winners. Consider how the burden on the workforce could be reduced with digital apps and AI-enabled patient engagements leveraging HIPAA-compliant natural language processing on existing voice platforms (e.g., Alexa). Such applications also free clinicians to operate at the top of their licenses. The next year will see many pilots of creative concepts in the space.
The tightening economic backdrop, alongside rising consumer expectations, more powerful technology and the prevalence of chronic conditions, will fuel further adoption of VBC models. Large employers wanting to know what they are getting from higher rates will be yet another prompt for innovation.
5. Consolidation Increases as Non-Traditional Players Press on
Challenging macroeconomic conditions will drive more consolidation and spark aggressive plays from tech platforms and large retailers. In this sense, 2023 will look a lot like recent years. Retailers and other non-traditional players are cracking the code on healthcare, faster than healthcare players are cracking the code on consumerism. Amazon, Walmart and other large players will continue experimenting on their own, buying up promising ventures and looking for partners that can further their huge ambitions.
And their ambitions won’t shrink just because the economy does. If you already thought these companies were relentless competitors when the economy was good, then you can expect them to press their advantages even more forcefully in pursuit of ever greater market share as cost and capital pressures rise for others.
FINAL THOUGHTS
The healthcare industry has seen plenty of change during the last few years. The next year will continue that trend. And as challenging as the economic conditions will be, healthcare leaders can drive change for the better by thinking boldly and targeting investments in the most promising areas of opportunity.
Contact our healthcare team today. We’d love to talk about the transformation opportunities at your organization.