BLOG
Nine Digital Shifts to Sustain B2B Companies During Trying Times Trends in Digital Innovation
Supply chains and alternative channels take on outsized importance.
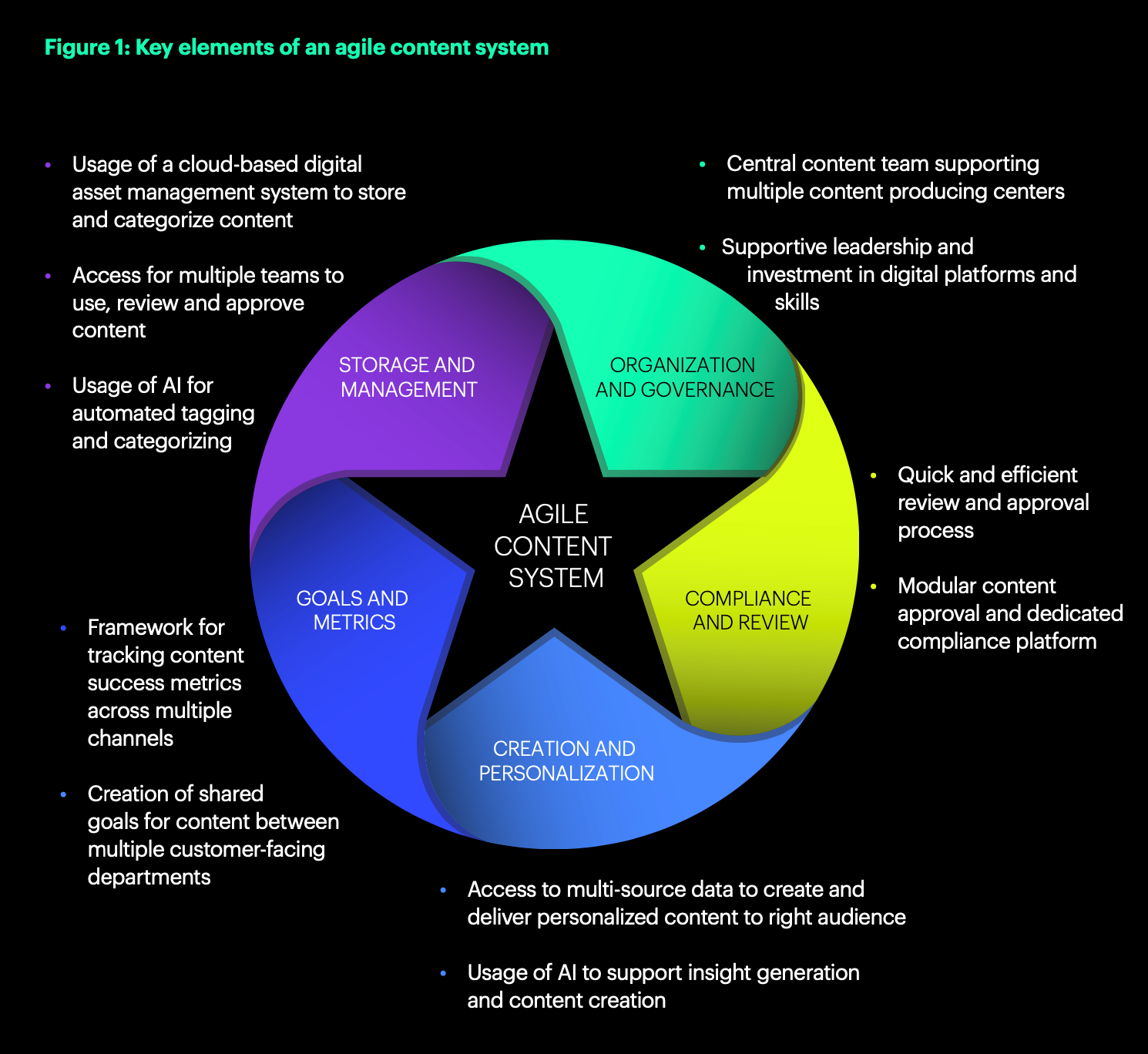
The biggest challenge for today’s businesses is to consistently produce personalized content at a large scale, deliver it at breakneck speed, and credibly have an impact on revenue. The businesses that are successful in this endeavor have invested in an innovative set of capabilities that make up an “Agile Content System”.
Digital transformation in normal times is usually considered a growth opportunity – and it is. B2B companies coping with the pandemic are also demonstrating that shifting to digital can provide important benefits in sustaining the business through:
- Alternative channels for customer engagement – the use of Zoom, Teams, Slack, and other forms of collaboration and meeting apps have skyrocketed
- Keep parts of the supply chain operating – ecommerce has proven less vulnerable to disruption than call center or face to face channels
- Lower costs – by using data analysis to uncover and target expense reduction
- Preserve cash flow through business model redesign – SaaS business models are providing a valuable cash flow buffer in the face of decelerating demand.
These benefits are crucially important in this unsettled period, but they will also be valuable once the crisis recedes. Digital marketing and selling, digital experience innovation and digital operating model renovation stand out as three digital transformation shifts that leaders can use to sustain their business as much as possible during this crisis as well as to accelerate customer demand once the economy rebounds.
Identifying and pursuing quick digital wins that can also elevate future performance has become an immediate imperative for B2B leaders. The purpose of this article is to provide guidance on where to look and what to prioritize in each of the three transformational shifts. Our recommendations are based on the discussions with B2B leaders and examination of successful cases of B2B digital transformation we conducted for our forthcoming book The Definitive Guide to B2B Digital Transformation
Digital Selling and Marketing:
In such uncertain times, the best customer for most B2B businesses is the customer they already have. Current customers are much more likely than new prospects to buy, have a lower cost to serve and will be more willing to endure the delays and interruptions their current suppliers encounter. Using collaboration and virtual meeting tools to enable sales teams and intermediaries to connect with buyers who are working from home is only a first step. Customers have a need to be connected to a bigger picture about what’s going on in the market, in the supply chain and even in different parts of their own company. They may require frequent updates on even small issues that previously wouldn’t garner their attention but are crucial to keeping their business afloat. And, customers need help to figure out new paths forward and rapidly find alternatives as business conditions change. There are several use cases to increase the use of digital to focus on existing buyers:
Account-Based Marketing (ABM) has never been more important. It is a superior way to coordinate the efforts of sales, digital marketing and service to meet the information and relationship needs of the full set of stakeholders, influencers and decision-makers in current accounts. ABM can be set up in the basic form in a matter of weeks and then can expand and grow. When the economy improves it can take on the added task of improving prospecting and new customer acquisition.
Digital customer insights and analytics become essential when the routine ways of monitoring a category through face-to-face interactions among industry ecosystem participants break down. Consider opening up an industry “war room” to buyers who can join virtually or receive insights through an email or online feed. Enable the war room with social listening, digital surveys, scouring the internet for news and monitoring key data sources. Once the current crisis is over the war room can become a source of insights for innovation or a value-added service that can build a competitive advantage.
Direct Ecommerce may be the only way to keep the parts, accessories and supplies flowing that keep customers in business. For service providers, it may take the form of shifting in-person services to digital channels. Barriers put up by intermediaries such as agents, distributors, and systems integrators can prevent suppliers from undertaking commerce directly with their customers. In times of crisis, these barriers will come down; enabling both supplier and customer to sustain a revenue stream while establishing a direct connection that will be very valuable, and hard to turn off, when conditions improve.
Digital Experience Innovation:
Most mid-size and large corporate customers have a built-in divide between the purchasing department and the user of the supplier’s goods and services. In situations like the pandemic, operations become more siloed and day-to-day connections between the buyer, supplier and user can fray. Users can feel isolated and unserved. Digital experience innovation plays a valuable role by meeting the needs of the user around the clock with less human intervention from the purchasing team or the supplier. The use cases for user support span the entire customer experience. They include:
Virtual Technical Support can be the lifeblood for corporate users struggling to find new ways of working and encountering new or unexpected bottlenecks as they try to patch together approaches to keep doing their jobs. B2B suppliers should consider ways to open up their expertise online. Can training guides, specification sheets, and other materials intended for the technical support team be made available to customers online? How about setting up a Virtual Technical Support SWAT team that can swoop in after an initial online meeting and use collaboration tools to solve complicated problems (systems integration challenges, supply chain workarounds, etc.) more quickly than normal? The service may be essential during the pandemic but could save travel and speed problem resolution when times return to normal. Collecting data on problems and their resolution can later enable AI-driven systems to automate the service in the future.
Online Learning becomes a necessity when there is no readily available source for corporate users to learn how to work with new components, become familiar with a crucial application, or manage a novel service because a supply chain disruption changed their normal routine. Avoid becoming entangled in long lead times to develop a new curriculum by setting up an online listening function to understand what challenges customers are facing. Then, empower sprint teams to create videos and audio-assisted documents to fill the need. The production flaws will be forgiven in a time when help will be so appreciated. Later on, the content can improve the larger curriculum and responsive listening can inform technical support and solution innovation.
A Digital Bulletin Board is an excellent and inexpensive way to keep customers informed of what’s going on from a supplier and industry point of view. It can span multiple topics from immediate steps to mitigate health challenges, to information about shortages or substitute offers to information about how others in the industry are coping with important challenges. It can be a tool for employees to stay informed as well as customers. At a time when many in an industry are looking inward, it can elevate the presence of the supplier within the customer as a source of information and expertise and provide a platform for continued use once the pandemic has receded.
“Digital marketing and selling, digital experience innovation and digital operating model renovation stand out as three digital transformation shifts that leaders can use to sustain their business as much as possible during this crisis as well as to accelerate customer demand once the economy rebounds.”
Digital Operating Model Renovation:
Many of the world’s companies may be heading for a cash crunch and resource imbalances over the next few months. Now may not be the time for thinking about how the operating model can be redesigned, pursue new customers, or enter new markets. It is time to consider important, and significant moves to improve the effectiveness and efficiency of the business in ways that will be sustainable for the next few years.
Subscription Revenue Models provide a more sustainable revenue stream in times of uncertainty and in normal times. They also lower the initial outlay customers must make for important purchases. A shift that can be extremely valuable for cash conserving customers. There is usually a huge timing hurdle to overcome when converting transactional purchases to subscriptions because large initial revenues must be given up by the supplier in favor of a revenue stream that is spread over months or years. This period of economic pause may be an ideal time to move to subscription because demand is already depressed, interest rates are low, and investors may be willing to endorse any move that sustains revenue. The long-term benefits will be substantial, and the normal short-term barriers may be easier to overcome.
Cost to Serve Reconfiguration is a topic, that although very sensitive, cannot be overlooked. In normal times it includes thinking through how automating processes or investing in new digital platforms can reduce labor costs and generate bottom-line savings. However, this is not the time to install major new systems or make uncertain employees fear for their jobs even more than they already do. It is the time to collect data, measure, and evaluate whether the new selling, marketing, technical support, online education and digital communication approaches can be optimized and scaled after the crisis has subsided to lower cost to serve, boost employee work-life balance and improve customer service. Treating the crisis as a series of pilots and experiences requires collecting data and measuring impact. The benefits for ongoing operations can be as profound as the short-term gains these changes produce.
Agile Process Redesign is at the heart of going faster and incorporating customers into the design process for many organizations. The importance of quickly bringing new solutions to market or rapidly adapting current solutions has been made abundantly clear in the past several weeks. Most corporate leaders have dramatically stepped up their planning but are struggling to accelerate the pace of the work that actually gets done. This is an ideal time to introduce agile teaming methods to the workforce. There is no shortage of projects that need rapid attention, the case for change is apparent to employees and these methods can be deployed quickly with fairly low investment. Agile methods have numerous additional benefits in driving leadership accountability, clarifying project status and ensuring that projects remain customer-focused even when moving rapidly. The payoff is immediate and the benefits for the organization when things improve are substantial.
By Fred Geyer (Prophet) and Joerg Niessing (INSEAD), authors of the forthcoming book The Definitive Guide to B2B Digital Transformation.
Watch this video to learn more.
FINAL THOUGHTS
The nine digital shifts described in this article are a starting point for thinking through moves to make to sustain B2B businesses in an unprecedented time while laying the groundwork for future success when this crisis recedes. We have tried to be pragmatic by recommending moves that can be implemented in the short term and will be valuable to customers, employees and the business for the future. This is not the time to wait. Leaders who act now can strengthen their options and improve their chances for success.
If you need help figuring out what path to take now, in the next 6-8 months, or beyond, please don’t hesitate to reach out. We’re happy to have a conversation. Also, if you have any questions you’d like answered by our experts, drop them into the comments below or reach out directly here.